Introduction to Radio Frequencies (RF)
Info
This note is still in development.
Sin waves -- lower frequencies have further throughput, but improved range.
- AM Frequencies: 540 kHz - 1700kHz
- FM Frequencies: 88 mHz - 108 MHz
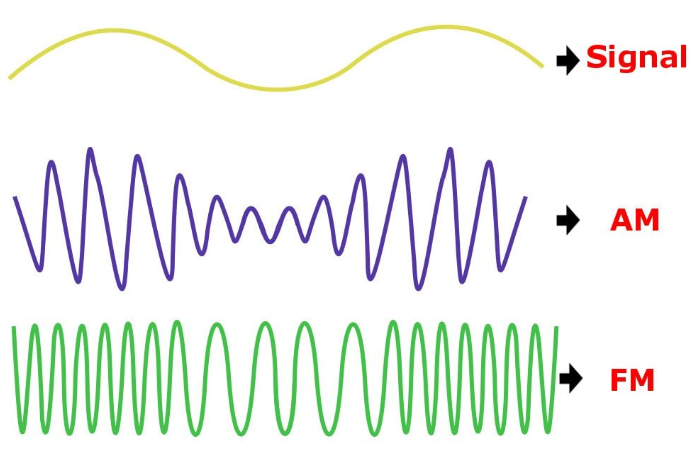
Determining RF Modulation is effectively a wireless version of a cable determining a BOD rate
Even /round numbers (outside of the AM/FM range) can be indicative of frequencies of interest, because nature doesn't really like pretty numbers.
Modulation Types:
- PSK = Phase Shift Key
- BPSK = Bi PSK (Binary Phase-Shift Keying)
- QPSK = Quad PSK (Quadrature Phase-Shift Keying)
- DQPSK = Diff-Quad PSK (Differential Quadrature Phase-Shift Keying)
Transceiver = Transmitter + Receiver
Transponder = Relay that can modify the frequency
Examples:
- HackRF = Transceiver
- RTLSDR = Receiver (should be at the event)
FCC ID codes can allow us to find the frequencies of transmitters, assuming we know what transmitter is being used
Order of Operations for Manipulation:
- Find frequency
- Determine Modulation
- Send data (manipulate)